Guide to Wire Rope
MENU
- Structural Wire Rope Applications
- Computer-Assisted Design and Detailing
- High Strength Structural Strand
- Custom Finishes
- Pre-stretching
- Striping
- Measuring Wire Rope
- Corrosion Protection
- End Terminations
- Attaching Sockets
- Proof loading
- Order Specifications
- Wire Rope Selection
- Rotation-Resistant Ropes
- Specialized Wire Rope
- Wire Rope Handling and Installation
- Standard Operating Practices
- Wire Rope Inspection
- Technical Info & Specifications
Wire Rope Lay
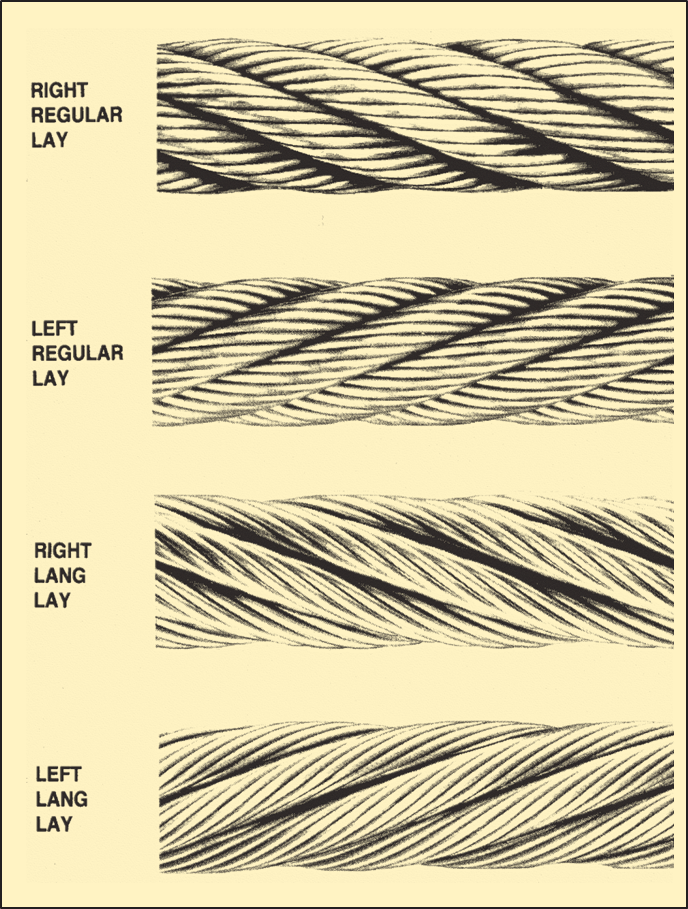
The helix or spiral of the wires and strands in a rope is called the lay.
Regular lay denotes rope in which the wires are twisted in one direction, and the strands in the opposite direction to form the rope. The wires appear to run roughly parallel to the center line of the rope. Due to the difference in direction between the wires and strand, regular lay ropes are less likely to untwist or kink. Regular lay ropes are also less subject to failure from crushing and distortion because of the shorter length of exposed outer wires.
Lang lay is the opposite; the wires and strands spiral in the same direction and appear to run at a diagonal to the center line of the rope. Due to the longer length of exposed outer wires, lang lay ropes have greater flexibility and abrasion resistance than do regular lay ropes. Greater care, however, must be exercised in handling and spooling lang lay ropes. These ropes are more likely to twist, kink and crush than regular lay ropes.
Right or left lay refers to the direction in which the strands rotate around the wire rope. If the strands rotate around the rope in a clockwise direction (as the threads do in a right hand bolt), the rope is said to be right lay. When the strands rotate in a counterclockwise direction (as the threads do in a left hand bolt), the rope is left lay.
Right regular lay is furnished for all rope applications unless otherwise specified.
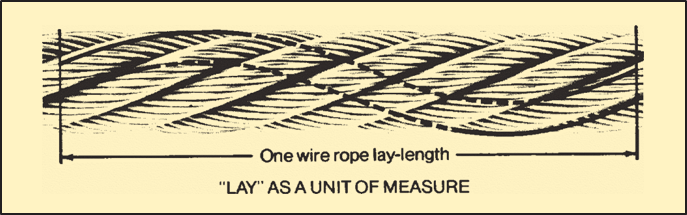
When a lay-length is used as a unit of measure, it refers to the linear distance a single strand extends in making one complete turn around the rope. Lay-length is measured in a straight line parallel to the center line of the rope, not by following the path of the strand. The appropriate time to replace a wire rope in service is frequently determined by counting the number of broken wires in the length of one rope lay.